SAFE
WORKING AT HEIGHT
Oleh : Bayu Nurwinanto
The purpose of this
manual is to eliminate potential harm to all employees, contractors and
visitors . resulting from persons falling from one level to another or being
affected by falling objects. It applies to :
- All operating sites and offices.
- All employees, contractors and visitors.
The manual requires
that a system of work for prevention of falls from height is established and
maintained in all work situations. This can be achieved through :
- Where practicable, the elimination of the need to work where there is the risk of a fall.
- Conducting risk assessments before the commencement of work and at any time the scopeof work changes or the risk of a fall increases.
- Selection of appropriate control measures using the hierarchy of controls.
- Ensuring all equipment used is fit for work.
- Ensuring all persons responsible for, or performing work, where there is a risk of falling, are competent in the correct use of the site management systems for the prevention of falls.
- Development of procedures for the use and disposal of all equipment that supports or lifts a person at height.
- The use of fall arrest equipment as the last option for a control measure (after all other control measures have been explored and deemed to be inappropriate), where it is not practicable to eliminate the risk of a fall.
WORK AT HEIGHT
“Work at Height” is
defined as whenever people are at risk of falling from, into or through one level
to another. No minimum height is stipulated as to when controls must be
implemented. If a person can fall from one level to another a risk assessment
must be completed.
FALL INJURY
PREVENTION SYSTEMS (FIPS)
Fall Injury Prevention Systems are systems
designed to arrest or prevent a person falling from one level to another,
whilst minimising the risk of injuries or harm during the fall. FIPS include
fall restraint systems, fall arrest systems, catch platforms, scaffolding,
safety nets and safety mesh.
RESTRAINT TECHNIQUE
A combination of anchorage placement and lanyard
length adjustment which will not physically permit the operator to reach a
fall-risk position unless the lanyard is incorrectly adjusted.
 |
(A) Restraint technigue adjustable lanyard
|
RESTRAINED FALL
A pole-strap of length
which will permit only a restrained fall when working on a pole.
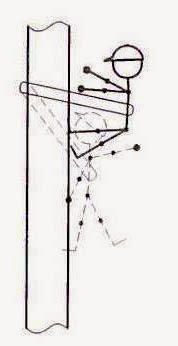 |
(B) Restraint Fall Polestrap
|
LIMITED
FREE FALL
A combination of anchorage placement and lanyard
length which will permit only a limited free fall (≤600 mm).
 |
(C) Limited Fall-Free distance ≤ 600
|
FREE FALL
Equip operators with personal fall-arrest
equipment which will not prevent a fall but minimise the risk of injury in the
event of a fall, maximum 2 metres free fall. This will likely involve static
lines or lanyards with shock absorbing devices.
 |
(D) Free fall-free fall distance >600
|
ANCHORAGE
POINT
A secure point of attachment on a structure to
which a safety harness or fall restraint / fall arrest device, or lanyard, or
lanyard assembly or static line may be secured.
SAFETY HARNESS
A full body harness
with a fall arrest attachment point at the top dorsal position, i.e. between shoulder
blades, which was manufactured and complies with AS1891.1 Industrial Fall
Arrest Systems and Devices - Safety Belts and Harnesses.
LANYARD
A lanyard is used to
connect a safety harness to an anchorage point or static line in situations
where there is a risk of a fall or when used in restraint mode to prevent a
fall. Lanyards can be either adjustable or fixed length and incorporate the use
of a shock absorber.
STATIC LINE (PERMANENT OR TEMPORARY)
A horizontal safety line or rail system to which
a lanyard may be attached and which is designed to arrest a free fall, as per
AS 1891.2 Industrial Fall Arrest Systems and Devices - Horizontal Lifeline and
Rail Systems.
TRAINING AND
COMPETENCY
All Team Leaders, Responsible Officers and
employees working at heights; or responsible for work carried out where there
is a risk of falling shall be competent in the correct use of the systems for the
prevention of falls.
Persons who are
exposed to the risk of falling shall:
- Be able to participate in the risk assessment of the work.
- Know and understand the control measures for fall prevention.
- Be competent in the correct use of those control measures e.g. All PPE and equipment.
- Have a current license, ticket or certificate of competency for any plant being used as a
- control measure e.g. EWP, scaffold etc.
OTHER RELATED TRAINING
Equipment training
linked to working safely at heights can include :
- Mobile Work Platforms.
- Scaffoldings.
- Rigging & Dogging.
RISK
ASSESSMENT
All persons required to perform work at
height must understand and actively participate in risk management processes.
HIERARCHY OF CONTROLS
Users of fall prevention equipment need to be
aware how these systems are placed within the hierarchy of control for fall
prevention, so that an assessment can be made as to whether the highest level
of practical protection practical is being applied in case. The hierarchy of
controls are.
Elimination - Eliminate the need to access
the fall-risk area, e.g. by locating and selecting items requiring inspection,
maintenance and other attention, elsewhere.
Substitution - Provide alternative means of
access to the point or item to which access must be made which avoids the risk
of a fall e.g. walkways or scaffolding.
Engineering / Isolation - Barricade or
enclose the fall-risk so that it cannot be reached by, hard bunting, handrail
scaffolding.
Administrative controls are required for all
steps; JSA’s or SOP, SWP for common tasks, training, signs etc.
Fall Prevention PPE - Must only be considered
as a last resort and only if all other control measures are impracticable,
unavailable or will introduce further hazards to the work. Provide PPE which
either prevents a fall or reduces risk or severity of a fall.
Persons shall calculate the actual distance
based on the equipment they will use prior to its use Figure for example :
ANCHOR POINTS
Anchor points are used to
attach Fall Arrest harness worn by a person via a connecting lanyard. Anchor
points used in Fall Injury Prevention Systems (FIPS) shall be assumed to
withstand the force of the load if a person was to fall. Anchor points for limited
or free fall.
- Shall be located above head height of the person and located in a central location (within 30 degrees from vertical) that prevents a pendulum swing.
- Shall have the required clearance below the worker for the type of system being employed (eg length of lanyard, plus tear out distance, height of user plus safety margin).
- Shall consist of a closed loop hook eye and must allow for the direct attachment of the safety device. Alternately, an endless loop lanyard can be wrapped around a suitable size steel structure (capable of holding 1500Kg) and the lanyard directly connected to both ends of the endless loop lanyard. Do not choke the endless loop lanyard.
- Can be a “Static Line” as long as it has been correctly designed and installed.
- Can be scaffold if correctly designed to be on anchor point.
- Pre-use inspection by the user.
- For permanent anchors in general areas a six (6) monthly formal, certified integrity check that is recorded.
Static lines are used
where a range of movement is required in one direction. A typical example being
when repairing or painting a roof where free movement along the roof is
required but persons need to be prevented from falling off the edge of the
roof. Static lines can be used as anchor points for either fall restraint or
fall arrest equipment.
They shall be either :
- Permanent 12mm diameter steel (generally stainless steel) cable attached to permanent anchors or;
- Temporary systems that use 20 mm diameter flexible rope that is suitable for such use. Natural fibre rope shall not be used.
Anchor points for
static lines shall be designed, approved and checked after installation by a
structural engineer.
A number of
commercial temporary static line systems are available which include attachment
and tensioning devices. Only those systems that comply with AS1891 shall be
used.
Maintenance of static
lines will depend on its frequency of use and where it is used. However, the
following is required:
- Pre-use inspection by the user.
- For permanent static lines a formal certified integrity check of the cable and anchors shall occur every six months and be recorded and the line tagged. Greater inspection frequency shall occur in aggressive environmental conditions.
- For temporary static lines, all components shall be checked prior to use, paying particular attention to any fraying, cracking or cuts in the rope be recorded and the line tagged. The attachments shall be checked for distortion, cracks or sharp edges where the rope contact occur.
- Emergency response coordinators shall be informed of each use of a static line system.
Lanyards are used to connect persons who are wearing either fall restraint or arrest equipment to an anchor point. There are several types, being fixed length, shock absorbing and inertia reel
retractable, which are detailed in the section below.
Those using a lanyard shall ensure that it is suitable for the proposed use and that it will provide the required fall restraint or arrest. All fall arrest situations shall require a shock absorber in the system.
Fixed length lanyards are used in either fall restraint or arrest situations. For fall restraint, the length needs to be such that, at maximum length, it prevents the person getting too close to any edge where the person could fall. For fall arrest, the summed length of the lanyard, the expanded shock absorber, the person and a one (1) metre safety margin, does not exceed the height that the person can fall.
Shock absorbing lanyards can be used in either total restraint or free fall arrest situations. Endless loop lanyards (snake slings) are used to wrap around structural beams etc. in order to provide an anchor point for either fall restraint or arrest. An endless loop lanyard shall not be choked (one end threaded through the other) rather both ends shall be placed in the attachment device of the attaching lanyard.
Lanyards must be
checked for compatibility of all components, including the harness attachment
point and anchor attachment point which must be with a Double Action Steel
Screw Gate type Karabiner to prevent the potential for either ‘Crush out’ or
‘Rollout’ occurring.
All lanyards, with the exception of the endless loop, shall be fitted with Double Action Steel screw gate karabiners. It is important to inspect the work area where the lanyards will be used to ensure that they will not be damaged by sharp edge on beams or sheet steel, dangle in pools of water, oils or chemicals and the karabiners do not become jammed up with dust or crushed rock.
Any Carabiners that are unable to be fully screwed closed shall be replaced immediately.
Maintenance on lanyards shall be :
- Pre-use visual inspection for cuts, abrasion, heat or oil or chemical damage and currency of operating life, which shall not exceed ten years from manufacture.
- Pre-use check of the condition of carabiners to ensure that they operate freely, do not jamb open and are not bent or damaged in any manner.
- For shock absorbing lanyards, a pre-use check that the shock absorber has not opened in any manner indicating that it has arrested a fall.
- A six monthly formal, certified integrity check by a registered organisation that shall be recorded and the lanyard tagged with date of inspection. This will be organised by the Emergency Services Coordinator in conjunction with Area Planners.
They are particularly suitable where good flexibility in a working area is required. They are advantageous where persons climb up and down a structure as part of their work tasks. They are also useful for low height fall arrest situations where other types of shock absorbers cannot be used.
Persons using an inertia reel lanyard shall :
- Conduct a pre-use inspection of the whole length of the inertia reel, checking for cuts and tears on fibre type and damaged, “bird caged” or broken wires on wire type device.
- Check the inspection tag to ensure that a formal inspection has occurred within the last 3 months.
- Check for damage on the housing and cable or fibre entry point.
- Check for the correct and immediate operation of the locking device when a quick pull is applied to it.
- A formal and documented inspection every three months conducted by a competent person.
- Annually an internal inspection of the device by an authorised service agent (in the absence of recommendations specified by the manufacturer) shall occur.
- Tagging and recording (log record) of the device to indicate that the inspection has occurred.
 |
| Figure 1 |
 |
| Figure 2 |


That’s great! Just pumped up. You always give your best!
ReplyDeleteSuper useful and awesome information here. I thank you! Thank you very much!
Have a look at our website to buy safety equipment's if you want.
Fall Arrest Harness and Lanyard
Slot City Casino: 70 Free Spins on Slots of Vegas - Mapyro
ReplyDeleteSlot 문경 출장샵 City is 경산 출장마사지 a fun and 나주 출장샵 fun casino that has been 포항 출장샵 around since 2012 and with a fantastic 영주 출장마사지 range of slots, jackpots and promotions.
Having a great training work safety should always be a priority among company owners. Than you for being such a great source for work safety resources and definitely I am learning a lot from you. I also found Executive Training School as great school that helps you get RIIWHS204E work safely at heights certificate.
ReplyDelete