IMPLEMENTATION OF HSE
STANDARD
Oleh : Bayu
Nurwinanto
HIERARCHY OF CONTROL
HIERARCHY OF RISK
CONTROL HSE
Elimination
Elimination of the
hazard of a tool, the material in the phase of the work process.
Substitution
Substitution of
tools, machines and materials based on results of the examination the HSE
officer.
Engineering
Eliminating or
reducing the severity of hazards through modification by redesigning machines,
tools and materials to be used in doing the work.
Administrative Control
Reduce the duration,
frequency and severity of exposure through :
- Changes in procedures and ways of working.
- Scheduling, job rotation, rest time.
success is highly dependent on,
- Supervision of the implementation of control systems.
- Behavior of workers.
PPE (Personal Protective
Equipment)
PPE is clothing or equipment designed to control risks to health and
safety in the workplace.
It includes :
- Eye protection (goggles, safety glasses).
- Hearing protection (ear plugs, ear muffs).
- Breathing protection (respirators, face masks, cartridge filters).
- Foot protection (safety boots).
- Head protection (hard hats, helmets, sun hats).
- Body protection (high-visibility garments, thermal wear, overalls, aprons, safety harnesses).
- Substances used to protect health (sun screen).
- Outer wear (reflective vests, fluoro jackets).
PPE is the least
satisfactory solution to health and safety problems in the workplace, as it
does not address the hazard it only
provides a shield to protect the worker.
PPE should therefore
be used in addition to other control measures that provide workers with a
higher level of safety, rather than replacing those measures.
HAZARD IDENTIFICATION
TECHNIQUES
Many tools can be used to identify hazards in the workplace. Several
methods / techniques as follows :
- Inspection.
- Survey.
- Observation.
- Questionnaire.
- Audit.
- Statistics.
Definition:
A
Job Safety Analysis (JSA) is a method that can be used to identify, analyze and
record 1) the steps involved in
performing a specific job, 2) the
existing or potential safety and health hazards associated with each step, and 3) the recommended action(s)/procedure(s)
that will eliminate or reduce these hazards and the risk of a workplace injury
or illness.
Hazard Types:
The following hazards should be considered when
completing a JSA :
- Impact with a falling or flying object.
- Penetration of sharp objects.
- Caught in or between a stationary/moving object.
- Falls from an elevated work platform, ladders or stairs.
- Excessive lifting, twisting, pushing, pulling, reaching, or bending.
- Exposure to vibrating power tools, excessive noise, cold or heat, or harmful levels of gases, vapors, liquids, fumes, or dusts.
- Repetitive motion.
- Electrical hazards.
- Light (optical) radiation (i.e. welding operations, etc.).
- Water (potential for drowning or fungal infections caused by wetness).
Conducting
the analysis :
- Select jobs with the highest risk for a workplace injury or illness.
- Select an experienced employee who is willing to be observed. Involve the employee and his/her immediate supervisor in the process.
- Identify and record each step necessary to accomplish the task. Use an action verb (i.e. pick up, turn on) to describe each step.
- Identify all actual or potential safety and health hazards associated with each task.
- Determine and record the recommended action(s) or procedure(s) for performing each step that will eliminate or reduce the hazard (i.e. engineering changes, job rotation, PPE, etc.)
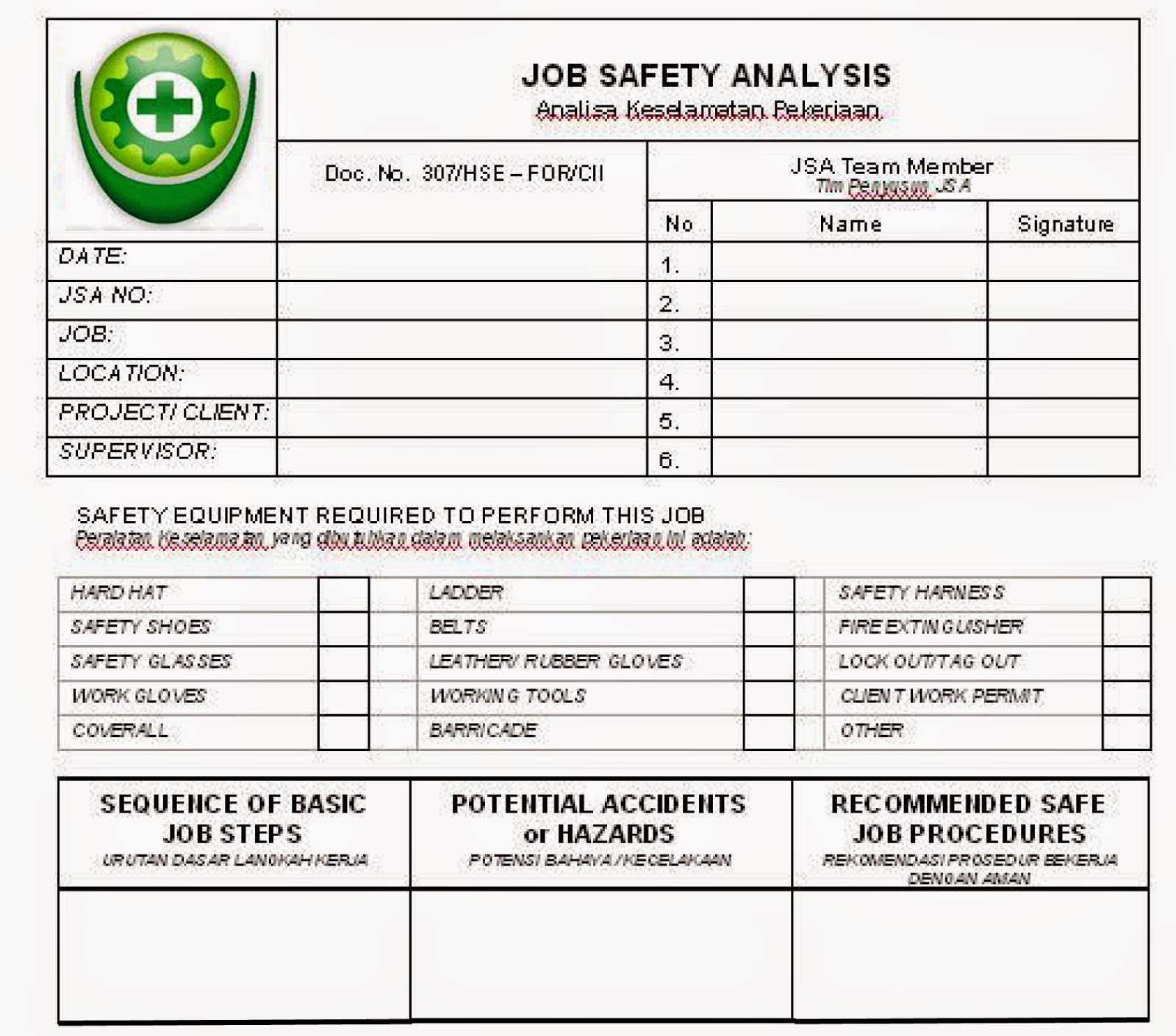
Examples of Job
Safety Analysis


Quality Control And Hes Engineering: Implementation Of Hse Standard >>>>> Download Now
ReplyDelete>>>>> Download Full
Quality Control And Hes Engineering: Implementation Of Hse Standard >>>>> Download LINK
>>>>> Download Now
Quality Control And Hes Engineering: Implementation Of Hse Standard >>>>> Download Full
>>>>> Download LINK ZP